Which Food Increases Platelets Level?

There are several foods that are believed to potentially help increase platelet levels, which are essential components of blood involved in blood clotting. However, it’s important to note that if you have a medical condition that affects your platelet levels, you should consult with a qualified healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Dietary changes alone may not be sufficient to address any underlying medical condition.
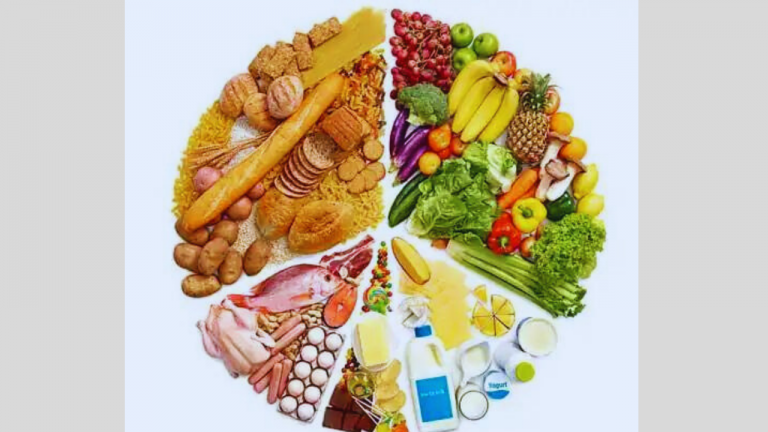
Some foods that are often associated with potential platelet-boosting properties include:
Leafy green vegetables: Spinach, kale, collard greens, and other leafy greens are rich in vitamin K, which is important for blood clotting and platelet function.
Vitamin C-rich foods: Citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and other foods high in vitamin C are believed to help increase platelet production.
Papaya and papaya leaf extract: Papaya and its leaf extract are known to have potential platelet-boosting properties and are used in some traditional medicine practices for this purpose.
Pumpkin seeds: Pumpkin seeds are a good source of zinc, which is important for platelet production.
Fish and omega-3 fatty acids: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and tuna are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are believed to have anti-inflammatory properties and may help promote healthy platelet levels.
Pomegranate: Pomegranate and its juice are rich in antioxidants and have been suggested to have potential benefits for platelet function.
Beetroot: Beetroot and its juice are known to be rich in iron and antioxidants, and may have potential benefits for platelet production.
It’s important to note that the scientific evidence supporting the direct effect of these foods on platelet levels is limited, and more research is needed to fully understand their potential impact. Additionally, individual responses to dietary changes may vary, and it’s important to consider overall dietary patterns and consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes or using foods as a sole treatment for any medical condition.